What is Machine Learning?

Machine Learning (ML) is a part of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that allows machines to learn without being expressly programmed to do so. It permits us to build a model that can learn from training data to make predictions based on the patterns recognized in the data.
Today, this allows for technological applications such as autonomous cars; recommendations for music, series, and movies based on our interests; fraud detection; and even image or voice recognition.
A bit of history
Machine Learning appears alongside computational machines. It arises collaterally when addressing the problem of mathematical decidability, the Entscheidungsproblem, formally proposed by David Hilbert. In 1937 the British mathematician Alan Turing designed a computing machine in which a paradox in its execution implied that mathematics was not decidable. This was a solution to this problem, and in addition, it laid the foundations of what would be the theory of modern computing.
In 1943, the neurologist Warren McCulloch and the mathematician Walter Pitts published an article in which they proposed the logical implementation of a biological neuron, on a Turing machine.
Developing this idea, Frank Rosenblatt proposed in 1958 the first neural network model, the Perceptron. These neural networks were the hegemonic technology until the 1990s. Due to the limited computing power of the computers of the time and the difficulty of performing statistical and mathematical analysis of neural networks, they caused the need for new methods of machine learning and new forms of analysis, such as Vapnik–Chervonenkis theory.
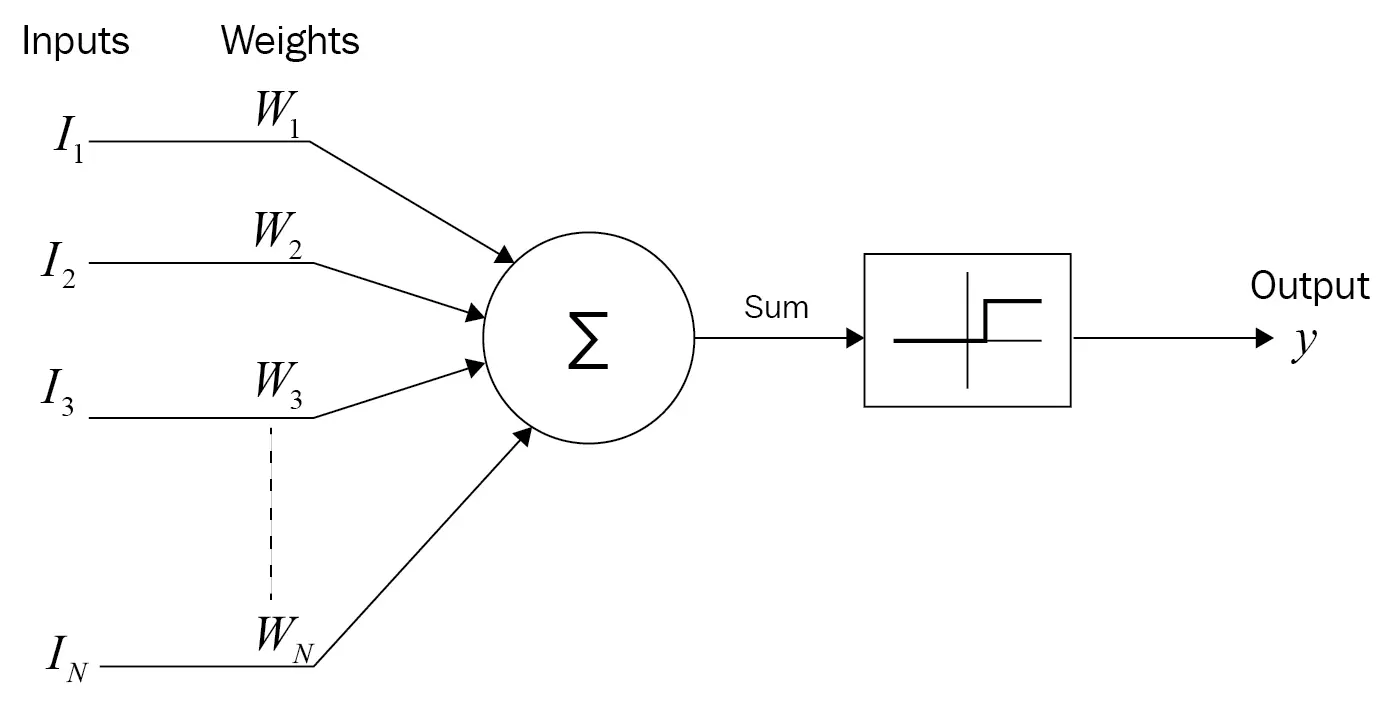
They had just created the foundation for neural networks and formally ushered in the age of Machine Learning.
ML model types
The different Machine Learning models can be classified into three large movements depending on the nature of the data received or the feedback of the model.
-
Supervised Machine learning: Considering the model as a black box, with an input and a certain output, in this case, given the training set with input and their corresponding outputs, the model is able to learn from the patterns recognized in this data and provide an inferred output for new inputs. Training data with input and output is called labeled data.
-
Unsupervised Machine learning: The data is unlabeled, this means that the model can find structures in the data by itself.
-
Reinforcement Machine learning: The machine learns through trial and error until it reaches the best way to complete a given task. The model learns from rewards based on its behavior.
Machine Learning is on the rise, during the last decade interest in it has grown and its adoption in the industry is total. The versatility it offers and its infinite applications make it not even seem that this trend will change. So what are you waiting for to learn more about it?